While many people have heard of Alzheimer’s disease and the memory problems it can cause, there are multiple other types of dementia that people should be aware of. One such for dementia is called vascular dementia. This is a form of dementia the results when people suffer multiple strokes. Most people understand that as people age, their chance of suffering a stroke increases. If these strokes occurred in multiple areas throughout the brain, this can result in a form of dementia.
There are many risk factors that people should be aware of that can cause blood clots. One of these risk factors is genetics. If there is a family history of blood clots in various areas throughout the body, the patient is at a higher risk of suffering a blood clot themselves. One of the other risk factors that can lead to blood clots is high blood pressure. When the blood vessels are exposed to high blood pressure, the vessels have to remodel to handle these increased forces. This remodeling can lead to a stiffening or closing of the blood vessel itself. This leads to an increased chance of suffering blood clots.
If blood clots form in the brain, this is called a stroke. The symptoms of vascular dementia can vary from Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia. This is because the symptoms will vary depending on where in the brain the strokes occur. The biggest landmark a vascular dementia is what is called a stepwise deterioration. While most people realize that Alzheimer’s disease is a gradual progression, the symptoms of vascular dementia will develop abruptly. This is because he sometimes will develop with each passing blood clot. With each stroke, the patient will suffer new symptoms. The symptoms will vary depending on the location in the brain of these blood clots strike.
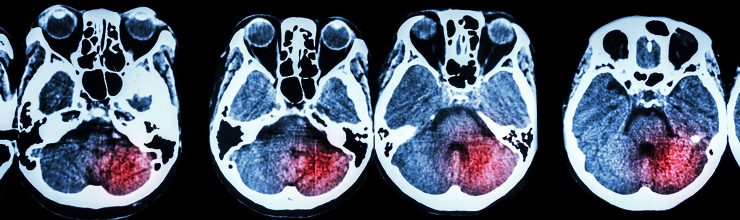
The diagnosis of vascular dementia is a combination of clinical correlation and imaging tests. The physician will take a detailed history to try and map out the timeline of the development of these symptoms. This history will reveal the stepwise progression of symptoms discussed above. Next, the physician is likely to order a round of imaging tests. CT scans and MRIs will likely reveal that the patient has suffered multiple strokes throughout the brain. This will confirm the diagnosis of vascular dementia along with the symptoms described above.
Finally, the treatment of vascular dementia is still in its infancy. There is some evidence to show that medications that treat Alzheimer’s disease, such as cholinesterase inhibitors, can have some benefit for the treatment of the symptoms associated with vascular dementia. Ultimately, the best treatment for vascular dementia is to prevent the disease from occurring in the first place. It is important that patients understand the risk factors and tailor their lifestyle to minimize these risk factors accordingly. For family members caring for patients who have vascular dementia, it is important to remain patient and compassionate. This will help the patient remain oriented to their surroundings and help to minimize symptom progression.


Leave a Reply